A normal antenatal check-up, also known as prenatal care, is a series of medical appointments and services provided to pregnant women to monitor and ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby throughout pregnancy. The specific content of a normal antenatal check-up may vary, but it generally includes the following components:
- Initial Consultation:
- Medical history review: The healthcare provider will inquire about the mother's medical history, including any pre-existing conditions, previous pregnancies, and family medical history.
- Pregnancy confirmation: Confirmation of the pregnancy, often through a urine or blood test.
- Regular Check-ups:
- Regular, scheduled visits: Throughout the pregnancy, the mother will have a series of check-ups, usually once a month initially and more frequently as the pregnancy progresses.
- Blood pressure monitoring: Regular measurement of blood pressure to detect and manage conditions like gestational hypertension or preeclampsia.
- Physical Examinations:
- Weight measurement: Regular tracking of weight gain to ensure it is within healthy limits.
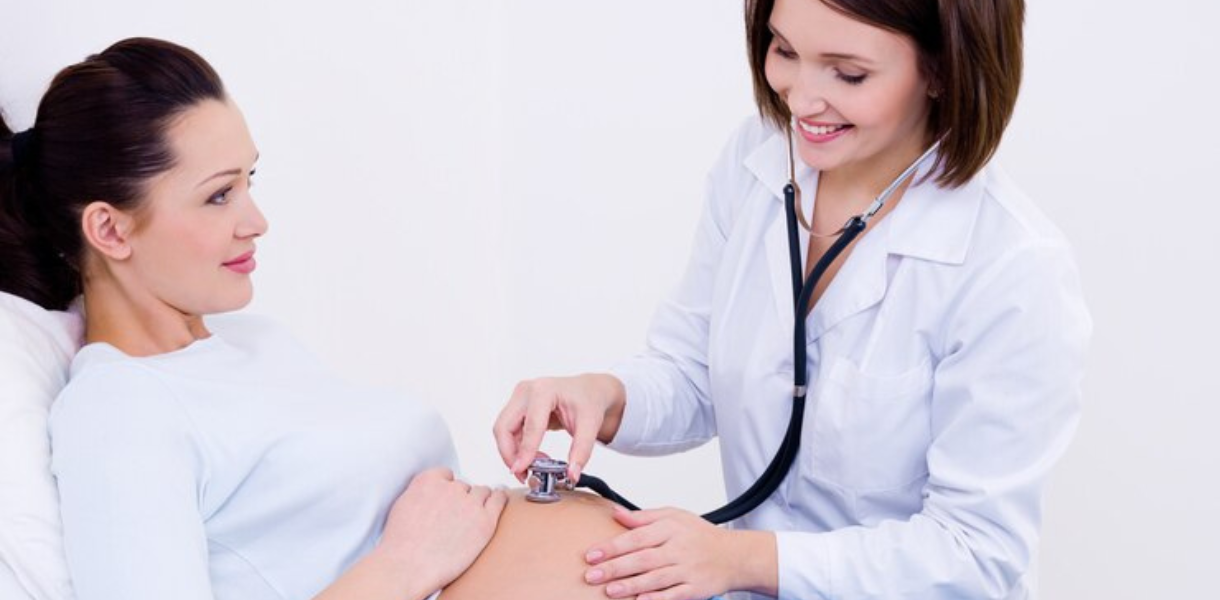
- Abdominal examination: Checking the size and growth of the uterus to assess fetal development.
- Fundal height measurement: Measurement of the distance from the pubic bone to the top of the uterus to estimate fetal growth.
- Fetal Monitoring:
- Fetal heart rate monitoring: Listening to the baby's heartbeat using a Doppler device or ultrasound.
- Ultrasound scans: Periodic ultrasound scans to monitor fetal growth, development, and to check for any abnormalities.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood tests: Routine blood tests to check for anemia, blood type, and Rh factor, as well as screening for certain infections.
- Glucose tolerance test: Screening for gestational diabetes.
- Urinalysis: Testing for conditions like urinary tract infections and preeclampsia.
- Educational Counseling:
- Nutrition advice: Guidance on maintaining a healthy diet during pregnancy.
- Lifestyle recommendations: Advice on exercise, rest, and avoiding substances harmful to pregnancy, such as alcohol and tobacco.
- Childbirth education: Information about labor, delivery, and postpartum care.
- Vaccinations:
- Administration of vaccines: Vaccinations such as the flu shot or the tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap) vaccine may be recommended during pregnancy.
- Discussion and Support:
- Addressing concerns: Discussing any concerns or questions the mother may have.
- Emotional well-being: Monitoring and addressing emotional well-being, including symptoms of anxiety or depression.
These components collectively contribute to ensuring a healthy pregnancy, monitoring potential complications, and preparing for a safe delivery. It's important for pregnant women to attend all recommended antenatal check-ups to receive appropriate care and support throughout their pregnancy journey.